Why is my check engine light on? Top reasons and fixes
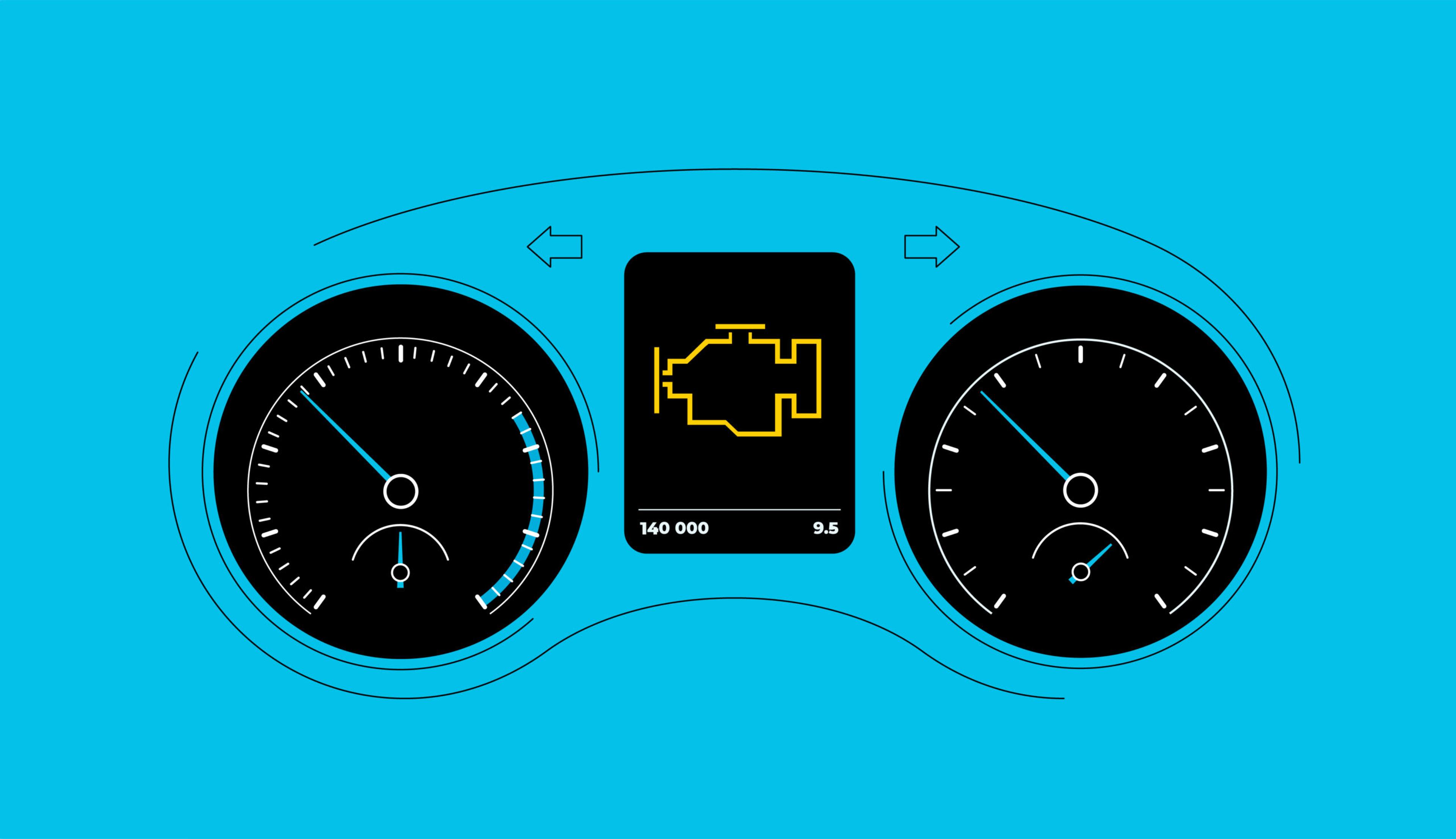
Every modern car has an engine-shaped warning light, which activates when something is wrong with your engine or other systems. It can mean anything from a loose gas cap to a blown head gasket, which is why vehicle owners often joke about this light being one of the most annoying things ever.
Owning a car is much easier if you understand why the check engine light comes on and how to deal with it.
Used cars have dark secrets
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
Flashing vs. static: how do I know if my check engine light is serious?
Depending on the severity of a situation, the check engine light can either flash or remain static.
A static check engine light warns about the need for servicing. Even if you don’t experience a loss of power or unusual engine noises, you should visit a repair shop as soon as possible. You can still drive, but you should postpone unnecessary trips to avoid further damage and safety risks.
Some of the problems that can cause a static check engine light are:
- Faulty sensors
- Engine misfire
- Low engine oil level
On the contrary, a flashing check engine light warns about more serious problems that can’t wait, such as misfiring cylinders, low engine oil pressure, or an incorrect combustion cycle.
It means that a car needs immediate repairs, therefore, you should pull over and tow a vehicle to a repair shop. Driving with a flashing check engine light can severely damage a car’s engine and other components.
Why do dashboard light colors matter?
You should also pay attention to the color of the check engine or other dashboard warning lights as they indicate the urgency of the issue:
- The red color is more serious and typically indicates critical alerts (equivalent to a flashing check engine light). It means that the problem could affect the safety or functionality of a vehicle and needs to be addressed immediately.
- An orange/yellow light is an advisory signal (similar to a static one) that is important but not critical. It suggests that the driver will need to take action at the earliest opportunity to prevent more serious problems.
Either way, you need to check the engine fault codes to address the problem properly.
How to reset the check engine light
Many drivers think fault code readers can solve issues by simply erasing codes. Unfortunately, these scanners are only diagnosing tools and someone still has to fix any revealed problems.
Here’s how to reset the check engine light properly.
Scan for trouble codes
Modern cars have advanced electric systems that you can scan using a trouble code reader. Most mechanics have these tools and will help you. Remember that not all scanners are equal – their cost varies between $10 and $20,000, with the more expensive options having more features, and providing faster/more precise operations.
The market is full of inexpensive code readers, meaning you can obtain the fault codes yourself. You only need to locate your car’s OBD II port (most commonly found beneath the steering wheel column), connect your tool, scan the vehicle, and see what codes come up.
You can research the codes on the internet for a more detailed explanation and potential solutions – this should give you at least a brief idea of the issue.
Diagnose the problem
Diagnosing the problem is more complicated than revealing the faults. If you’re lucky, a fault code will lead you straight to the problem. However, more often, it will only tell you that, for instance, the fuel pressure is too low. In turn, this could signal anything from a dirty fuel filter to a worn out fuel pump.
Here are the most common trouble spots with their respective fault codes:
- Faulty mass airflow sensor (P0101). A mass airflow sensor (MAF) measures the amount of air entering your engine, and the engine control unit (ECU) uses this data to provide the engine with the correct amount of fuel.
- Faulty oxygen sensor (P0131, P0134). It measures the proportion of oxygen to gas inside a vehicle's exhaust system to determine the correct air-fuel ratio. You may notice a significant drop in fuel economy when this sensor fails.
- Loose gas cap (P0455, P0457). When a car detects fuel vapor escaping the tank, a loose gas cap is one of the most common issues. The gas cap may even be faulty, meaning you’ll need to replace it.
- Vacuum leak (P0171, P0174, P2279). Vacuum leaks can cause many issues, triggering various fault codes. Some cars require there to be a vacuum to control the brake booster, turbocharger, or to adjust the air-fuel mixture. As a result, “lean air-fuel mixture” fault codes are common.
- Stuck EGR valve (P0401). An exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve reduces emissions by letting exhaust gasses pass into an air intake manifold for repeated use. This valve often sticks or fails, resulting in a loss of power and the P0401 fault code.
- Engine misfire (P0300). An engine misfires because of worn spark plugs, spark plug wires, or fuel injectors. It causes car shaking, rough idling, a loss of power, and excessive fuel consumption.
- Catalytic converter failure (P0420). The catalytic converter filters out harmful particles and burns them up, significantly reducing emissions. The check engine light can be triggered if the catalytic converter is missing or clogged up.
These are only a few of hundreds of possible fault codes, therefore, good knowledge is essential when working on modern cars. After obtaining the diagnostic trouble codes, a mechanic usually performs a live data check to determine which readings are out of order and which components should be inspected.
Fix it
Fixing the revealed problems means replacing broken parts and sensors, repairing wires, or cleaning electrical terminals. You could scan the fault codes and perform a few basic checks yourself. However, most repairs require special tools and knowledge, so you should leave them to professionals.
Bear in mind that most of the serious issues occur due to a lack of maintenance, therefore, proper car maintenance is needed to keep your car’s condition in top shape. For instance, oil changes extend the lifetime of your engine, a fresh coolant prevents overheating, and a new battery prevents internal damage. Those who follow a proper maintenance schedule have a much lower chance of facing major car problems.
Check engine light is more common on high-mileage vehicles
Since an engine light appears when something malfunctions or breaks down, it’s more common in high-mileage cars. It can even appear every 50,000 or 60,000 miles on some cars, alerting the driver: “Hey, I’ve been serving you this long. Now it’s time for a check-up.”
So, before making any assumptions, you should evaluate the mileage of your car.
Even if you think your car’s mileage is low, mileage rollbacks and other scams are very common in the used car market. To avoid them, always take the car for a professional inspection and check its history before handing over the money.
Full vehicle history reports can reveal surprising facts about mileage history, car accidents, and thefts, helping you to choose the next car or maintain yours. Simply get the car’s VIN number and enter it into the VIN decoder.

Check your VIN
Avoid costly problems by checking a vehicle's history. Get a report instantly!
